
 ','..','$myPermit') ?>SYLLABUS Previous: 10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols
','..','$myPermit') ?>SYLLABUS Previous: 10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols
10.1 Glossary of keywords
Slide : [
a-f -
g-u -
r-z ||
GLOSSARY:
Bloomberg -
Economist ||
DATA
]
100) echo "
";
?>-
Accrual period
- Time interval between the payment of bond coupons or swap settlements.
-
American exercise style
- Contract that can be exercised at any time during its life.
-
Arbitrage
- Trading strategy taking advantage of the price difference of two or
more securities to make an immediate (risk free) profit.
-
Arbitrageur
- Person who uses arbitrage as a trading strategy to make immediate
(risk free) profits.
-
Asset
- Something of value, a property owned by a person or a company.
-
Bear
- Animal used as a symbol when the market prices are falling in an economic
downturn.
-
Bid price
- The price a potential buyer is willing to pay for a security.
-
Boundary conditions (natural / essential)
- Conditions (usually justified by no-arbitrage arguments) that are imposed
on the boundary of the domain where the solution of a differential equation
is sought. Natural conditions are usually imposed through a surface term
after partial integration; essential conditions are imposed explicitly in
the linear system by replacing an equation by the condition.
-
Broker
- Individual who buys and sells goods for other persons.
-
Bull
- Animal used as a symbol when the market prices are rising in an economic
upturn.
-
Call option
- Security giving its holder the right and no obligation to buy an underlying
asset.
-
Cap
- Collection of caplets maturing at different
times.
-
Caplet
- Interest rate option providing for an upper limit on the interest rate;
a caplet entitles the holder to the difference between the spot rate and
the strike if this is positive, or zero otherwise.
-
Capital
- Amount of money that is invested or used to start a business.
-
Capital gain
- Amount of cash raised by the original owners who sell shares in the
initial public offering (IPO) of a company.
-
Capital asset pricing model (CAPM)
- Linear fit measuring the relative performance of a portfolio in
comparison with a market index average.
-
Capitalism
- Economic system in which a country's business and industry is controlled
and run for profit by private owners.
-
Clearing margin
- A margin deposit by a member of a clearing house (e.g. a broker) that
guarantees the performance of all the parties in a financial transaction.
-
Collar
- Interest rate option combining a cap and a
floor used as an insurance to guarantee
that the interest rates remain within a certain interval.
-
Commission
- Part of a cost that is proportional to the total value of a trade.
-
Contingent claims
- A demand that can be made only if one or more specified outcomes occur.
-
Coupon
- Predetermined amount of cash payed as an interest during the life of a bond.
-
Covered
- A written option is covered if the writer also has an opposing market
position on a share-for-share basis in the underlying security.
-
Delivery date
- The date when a
forward or
futures
contract ends with an amount of cash payed in exchange for the
underlying asset.
-
Delivery price
- Amount of cash in a forward contract
that will be payed on the
maturity date
in exchange of the
underlying asset.
-
Derivative
- Financial instrument whose value is derived from another asset.
-
Deterministic
- Which can be predicted with certainty from the past.
-
Discount
- Amount below the par value; difference between a bond principal and the
present value.
-
Discount bond
- Zero coupon bond.
-
Discount factor
- Present value of EUR 1 received some time in the future.
-
Discount function
- Function measuring the present value of one unit due at a later time.
-
Distribution (log-normal)
- Function measuring the probability density of an event using a log-normal
law; incremental changes of stock prices are almost log-normally
distributed.
-
Distribution (normal)
- Function measuring the probability density of an event using the famous
bell-shaped curve; incremental changes of bond prices are sometimes normally
distributed.
-
Diversification
- Dividing the investment into a variety of securities.
-
Dividend
- Portion of a company's profits payed out in cash to the shareholders.
-
Drift
- Slow systematic movement in the same direction.
-
Efficient market
- Economy in which prices immediately and fully reflect all relevant
information.
-
Efficient frontier
- In the modern portfolio theory, it is the locus of all the portfolios
where the highest possible return is achieved after reducing the
specific risk through diversification.
-
Entrepreneur
- Person who tries to make money by starting or running a business, especially
when this involves taking a financial risk.
-
Equilibrium swap rate
- Fixed coupon making the swap worthless when it is initially issued.
-
European exercise style
- Contract that can be exercised only at the expiry date.
-
Exercise an option
- Use the right to exchange the underlying for a fixed amount of cash.
-
Exercise (or strike) price
- The price at which the underlying may be bought or sold.
-
Exotic option
- Option that is not plain vanilla and is generally not traded on an exchange.
-
Expected value
- Average value obtained by weighting
possible realizations by their
probabilities.
-
Expiry time
- Date when an option contract ends.
-
Face (or principal) value
- Amount of cash an issuer (borrower) agrees to pay at the maturity.
-
Fannie Mae
- US government-sponsored federal national mortgage association.
-
Fee
- Part of a cost that does not depend on the total value of a trade.
-
Fixed income instruments
- Bonds and preferred stock that pay a predetermined amount of cash.
-
Fixed interest rate
- Predetermined return on investment of a bond, which remains independent of
the market spot rate.
-
Fixed leg (of a swap)
- Part of the contract involving payments that are predetermined (risk-free)
and remain independent of the spot rate.
-
Floating leg (of a swap)
- Part of the contract involving payments that depend on the spot rate and
therefore carry a financial risk.
-
Floor
- Collection of floorlets maturing at different
times.
-
Floorlet
- Interest rate option providing for a lower limit on the interest rate;
it entitles the holder to the difference between the strike and the spot
rate if this is positive, or zero otherwise.
-
Forward rate
- Interest
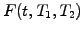 payed today at time
payed today at time 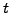 for a loan with a specified
maturity
for a loan with a specified
maturity 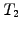 and starting at some point in the future
and starting at some point in the future 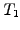 , where
, where
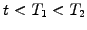 .
.
-
Forward rate agreement (FRA)
- Agreement to borrow or lend an amount of cash some time in the future
at an interest rate that is fixed today.
-
Forward contracts
- Agreement between a buyer and a seller to exchange certain goods for
a fixed price some time in the future.
-
Forward price
- The delivery price in a forward contract chosen so as to make it worthless.
-
Freddie Mac
- US government-sponsored federal home mortgage loan corporation.
-
Futures contract
- Special type of standardized forward contract
enabling anonymous trades on an exchange with a protection against defaults
through a clearing margin.
-
Gearing
- Strategy increasing the return of portfolio by increasing the investment risk.
-
Gross domestic product (GDP)
- Total value of goods and services produced by a country.
-
Go long
- Purchase an asset in exchange of cash.
-
Go (or sell) short
- Sell an asset that has been borrowed from another investor.
-
Hedger
- Person who buys securities to reduce the investment risk in a portfolio.
-
Hedging
- Strategy reducing the investment risk of a portfolio at the expense of
smaller returns.
-
Holder
- The purchaser of an option.
-
Implied volatility
- Volatility of an underlying asset, as
measured from the price of derivatives assuming a standard pricing model.
-
In-the-money
- Subset of an option series that has a finite
intrinsic value
that is payed out to the holder at the expiry.
-
Initial / Terminal conditions
- Value of a function of time that is known at the beginning of a calculation.
-
Initial public offering (IPO)
- First sale of a company's shares to the public.
-
Intrinsic value
- The value of an option if it would expire with the underlying at its current
price.
-
Investor
- Person or organization that buys property in the hope of making a profit.
-
Investment
- Money used to realize a project in the hope of making a profit.
-
Itô's lemma
- Mathematical formula relating the differential of a stochastic function
to differential of its stochastic arguments.
-
London inter bank offered rate (LIBOR)
- The rate of interest that major international banks in London charge
each other for borrowings.
-
Market
- Occasion when people buy and sell goods.
-
Market maker
- Person who's job it is to determine a fair price of a certain asset
and to help buyers and sellers exchange that over-the-counter outside
the market.
-
Market price of risk
- Parameter measuring how much the investors are risk seeking or risk averse.
-
Market value
- Spot price obtained via offer and demand
from sellers and buyers on the market.
-
Markov process
- Stochastic process where consecutive increments are independent from the past.
-
Martingales
-
Maturity date
- The end of the life of a contract.
-
Maximum likelyhood estimation
- Statistical method built so as to maximize the chance that a model fits
a given dataset.
-
Mean reversion
- Tendency of a quantity to evolve towards a long term average.
-
Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT)
- Description of rational investment choices based on risk-return trade-offs
and efficient diversification.
-
Monte-Carlo simulation
- Computer calculation performed with a crowd of random walkers to
statistically sample the evolution of market prices by adding small
increments.
-
Net asset Value (NAV)
- Total value of the fund's investment.
-
Notional principal
- The amount of cash used to calculate the payments in an interest rate swap;
the principal is ``notional'' because it is never really exchanged.
-
Numeraire asset
- Arbitrary asset chosen to measure the relative performance of an investment
in dimensionless units.
-
Offer price
- The price a seller is asking in exchange for a security.
-
Open-end fund
- Mutual fund where the holdings are continually reinvested and new shares
are created on demand.
-
Option
- Security giving its holder a right, but not the obligation, to buy or
sell an asset at a set price on or before a given date.
-
Option class
- Options having the same underlying and the same type of contract (put, call, etc).
-
Option series
- Option from the same class having the
same exercise price and expiry date.
-
Out-of-the-money
- Subset of an option series that has no
intrinsic value
and expires worthless.
-
Over-the-counter (OTC)
- Non-standard exchange of goods carried out between two parties outside
the market, generally without disclosing the price to the public.
-
Par
- Equal to the principalkeywd:principal or face value of a security.
-
Parameters: financial / numerical
- Financial parameters entirely specify the problem; numerical parameters
only serve to control the calculation and should never affect the result.
-
Path dependent option
- Option with a payoff depending on the price history of the underlying.
-
Portfolio
- Set of shares and financial instruments held by a person or an organization.
-
Possible realizations
- Outcomes of a random variable that have a finite probability to occur.
-
Premium
- Amount that is in excess of the par value, i.e. the positive difference
between the present value and the nominal principal value.
-
Principal (or face) value
- Amount of cash an issuer (borrower) agrees to pay at the maturity.
-
Principal components
- Partly uncorrelated random varialbles that can explain most of the
statistical observations from the markets.
-
Probability
- Measure of the likelihood that something will occur.
-
Put-call parity
- Relation between the price of vanilla options with the same strike price
and expiry.
-
Put option
- Security giving its holder the right and no obligation to sell an underlying
asset.
-
Random
- Which cannot be predicted with certainty from the past.
-
Redemption date
- Date when a debt security is has to be payed back, marking the end of the
lifetime of a bond.
-
Random walk
- Unpredictable motion resulting from increments that are generally assumed
to be independent of the past (Markov property).
-
Reset and payment times
- Beginning and end of the time interval
(accrual period)
between the payment of coupons in a bond or the exchange of interest
payments in a swap.
-
Risk
- The possibility of something bad happening sometime in the future.
-
Risk premium
- Reward the investors ask for taking a larger investment risk.
-
Security
- Document proving that somebody is the owner of certain goods or has a
right to acquire them in the future.
-
Smile
- Graph with a minimum implied volatility
for an underlying at-the-money.
-
Specific risk
- The uncertain outcome of an investment can be divided in specific and
non-specific risks. Specific risk can entirely be eliminated through
combination of anti-correlated assets and diversification; non-specific
risk affects the entire market.
-
Speculator
- Person who buys and sells goods in the hope of making a profit from
his view on the evolution of the market.
-
Split
- When a growing company emits new shares to reduce the price quoted in
the market. In a 2-for-1 split, 2 new shares are exchanged for every
share that was previously owned.
-
Spot
- The value for immediate delivery.
-
Stochastic
- Something that includes an unpredictable random component.
-
Strike (or exercise) price
- The price at which the underlying may be bought or sold.
-
Suzerain
- In the Middle Ages, the suzerain was a person who owned the right over
another (called the vassal) who promised to fight and be loyal in
return for being given land to live on.
-
Swap (of interest rates, currency exchange rates, etc)
- Contract whereby two parties agree to exchange, at known dates in the future,
a fixed for a floating set of rates without ever exchanging the principal.
-
Tenor of a bond
- Time interval between the payment of consecutive coupons.
-
Term structure of interest rates
- Interest rates calculated for bonds of different maturities.
-
Time value
- Difference between the intrinsic value
and the value of an option before it expires.
-
Transaction costs
- The cost of carrying out a trade (fees, commissions, plus the difference
between the price obtained and the middle of the bid-offer prices quoted
on the market).
-
Treasury rate
- Interest rate payed by the central bank responsible for a given currency.
-
Tree
- Method to approximate a dynamical system by recursively adding / subtracting
a fixed number of increments to all the possible outcomes.
-
Underlying
- Security that parties agree to exchange under conditions in a derivative
contract.
-
Vanilla
- Simplest form of a contract.
-
Venture capital
- High risk investment given in return for a participation in the control
and the future earnings of a start-up company that develops a new product.
-
Volatility
- A measure of the uncertainty of the price of an asset.
-
Wiener process
- Markov process where the increments are normally distributed with zero
mean and a variance proportional to the time step.
-
Writer
- The seller of an option, usually a large financial institution.
-
Zero-coupon bond
- A bond without coupon, where the principal and the interest are paid
at the maturity date.
-
Zero-sum game
- Game where the earning from one player exactly equals the loss from another.
SYLLABUS Previous: 10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols


 ','..','$myPermit') ?>SYLLABUS Previous: 10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols
','..','$myPermit') ?>SYLLABUS Previous: 10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols