
 HREF="sec10.html">10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols
HREF="sec10.html">10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols
10.1 Glossary of keywords
Slide : [
a-f -
g-u -
r-z ||
GLOSSARY:
Bloomberg -
Economist ||
DATA
]
Accrual period
Time interval between the payment of bond coupons or swap settlements.
American exercise style
Contract that can be exercised at any time during its life.
Arbitrage
Trading strategy taking advantage of the price difference of two or
more securities to make an immediate (risk free) profit.
Arbitrageur
Person who uses arbitrage as a trading strategy to make immediate
(risk free) profits.
Asset
Something of value, a property owned by a person or a company.
Bear
Animal used as a symbol when the market prices are falling in an economic
downturn.
Bid price
The price a potential buyer is willing to pay for a security.
Boundary conditions (natural / essential)
Conditions (usually justified by no-arbitrage arguments) that are imposed
on the boundary of the domain where the solution of a differential equation
is sought. Natural conditions are usually imposed through a surface term
after partial integration; essential conditions are imposed explicitly in
the linear system by replacing an equation by the condition.
Broker
Individual who buys and sells goods for other persons.
Bull
Animal used as a symbol when the market prices are rising in an economic
upturn.
Call option
Security giving its holder the right and no obligation to buy an underlying
asset.
Cap
Collection of caplets maturing at different
times.
Caplet
Interest rate option providing for an upper limit on the interest rate;
a caplet entitles the holder to the difference between the spot rate and
the strike if this is positive, or zero otherwise.
Capital
Amount of money that is invested or used to start a business.
Capital gain
Amount of cash raised by the original owners who sell shares in the
initial public offering (IPO) of a company.
Capital asset pricing model (CAPM)
Linear fit measuring the relative performance of a portfolio in
comparison with a market index average.
Capitalism
Economic system in which a country's business and industry is controlled
and run for profit by private owners.
Clearing margin
A margin deposit by a member of a clearing house (e.g. a broker) that
guarantees the performance of all the parties in a financial transaction.
Collar
Interest rate option combining a cap and a
floor used as an insurance to guarantee
that the interest rates remain within a certain interval.
Commission
Part of a cost that is proportional to the total value of a trade.
Contingent claims
A demand that can be made only if one or more specified outcomes occur.
Coupon
Predetermined amount of cash payed as an interest during the life of a bond.
Covered
A written option is covered if the writer also has an opposing market
position on a share-for-share basis in the underlying security.
Delivery date
The date when a
forward or
futures
contract ends with an amount of cash payed in exchange for the
underlying asset.
Delivery price
Amount of cash in a forward contract
that will be payed on the
maturity date
in exchange of the
underlying asset.
Derivative
Financial instrument whose value is derived from another asset.
Deterministic
Which can be predicted with certainty from the past.
Discount
Amount below the par value; difference between a bond principal and the
present value.
Discount bond
Zero coupon bond.
Discount factor
Present value of EUR 1 received some time in the future.
Discount function
Function measuring the present value of one unit due at a later time.
Distribution (log-normal)
Function measuring the probability density of an event using a log-normal
law; incremental changes of stock prices are almost log-normally
distributed.
Distribution (normal)
Function measuring the probability density of an event using the famous
bell-shaped curve; incremental changes of bond prices are sometimes normally
distributed.
Diversification
Dividing the investment into a variety of securities.
Dividend
Portion of a company's profits payed out in cash to the shareholders.
Drift
Slow systematic movement in the same direction.
Efficient market
Economy in which prices immediately and fully reflect all relevant
information.
Efficient frontier
In the modern portfolio theory, it is the locus of all the portfolios
where the highest possible return is achieved after reducing the
specific risk through diversification.
Entrepreneur
Person who tries to make money by starting or running a business, especially
when this involves taking a financial risk.
Equilibrium swap rate
Fixed coupon making the swap worthless when it is initially issued.
European exercise style
Contract that can be exercised only at the expiry date.
Exercise an option
Use the right to exchange the underlying for a fixed amount of cash.
Exercise (or strike) price
The price at which the underlying may be bought or sold.
Exotic option
Option that is not plain vanilla and is generally not traded on an exchange.
Expected value
Average value obtained by weighting
possible realizations by their
probabilities.
Expiry time
Date when an option contract ends.
Face (or principal) value
Amount of cash an issuer (borrower) agrees to pay at the maturity.
Fannie Mae
US government-sponsored federal national mortgage association.
Fee
Part of a cost that does not depend on the total value of a trade.
Fixed income instruments
Bonds and preferred stock that pay a predetermined amount of cash.
Fixed interest rate
Predetermined return on investment of a bond, which remains independent of
the market spot rate.
Fixed leg (of a swap)
Part of the contract involving payments that are predetermined (risk-free)
and remain independent of the spot rate.
Floating leg (of a swap)
Part of the contract involving payments that depend on the spot rate and
therefore carry a financial risk.
Floor
Collection of floorlets maturing at different
times.
Floorlet
Interest rate option providing for a lower limit on the interest rate;
it entitles the holder to the difference between the strike and the spot
rate if this is positive, or zero otherwise.
Forward rate
Interest
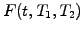 payed today at time
payed today at time 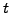 for a loan with a specified
maturity
for a loan with a specified
maturity 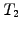 and starting at some point in the future
and starting at some point in the future 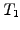 , where
, where
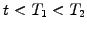 .
.
Forward rate agreement (FRA)
Agreement to borrow or lend an amount of cash some time in the future
at an interest rate that is fixed today.
Forward contracts
Agreement between a buyer and a seller to exchange certain goods for
a fixed price some time in the future.
Forward price
The delivery price in a forward contract chosen so as to make it worthless.
Freddie Mac
US government-sponsored federal home mortgage loan corporation.
Futures contract
Special type of standardized forward contract
enabling anonymous trades on an exchange with a protection against defaults
through a clearing margin.
Gearing
Strategy increasing the return of portfolio by increasing the investment risk.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
Total value of goods and services produced by a country.
Go long
Purchase an asset in exchange of cash.
Go (or sell) short
Sell an asset that has been borrowed from another investor.
Hedger
Person who buys securities to reduce the investment risk in a portfolio.
Hedging
Strategy reducing the investment risk of a portfolio at the expense of
smaller returns.
Holder
The purchaser of an option.
Implied volatility
Volatility of an underlying asset, as
measured from the price of derivatives assuming a standard pricing model.
In-the-money
Subset of an option series that has a finite
intrinsic value
that is payed out to the holder at the expiry.
Initial / Terminal conditions
Value of a function of time that is known at the beginning of a calculation.
Initial public offering (IPO)
First sale of a company's shares to the public.
Intrinsic value
The value of an option if it would expire with the underlying at its current
price.
Investor
Person or organization that buys property in the hope of making a profit.
Investment
Money used to realize a project in the hope of making a profit.
Itô's lemma
Mathematical formula relating the differential of a stochastic function
to differential of its stochastic arguments.
London inter bank offered rate (LIBOR)
The rate of interest that major international banks in London charge
each other for borrowings.
Market
Occasion when people buy and sell goods.
Market maker
Person who's job it is to determine a fair price of a certain asset
and to help buyers and sellers exchange that over-the-counter outside
the market.
Market price of risk
Parameter measuring how much the investors are risk seeking or risk averse.
Market value
Spot price obtained via offer and demand
from sellers and buyers on the market.
Markov process
Stochastic process where consecutive increments are independent from the past.
Martingales
Maturity date
The end of the life of a contract.
Maximum likelyhood estimation
Statistical method built so as to maximize the chance that a model fits
a given dataset.
Mean reversion
Tendency of a quantity to evolve towards a long term average.
Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT)
Description of rational investment choices based on risk-return trade-offs
and efficient diversification.
Monte-Carlo simulation
Computer calculation performed with a crowd of random walkers to
statistically sample the evolution of market prices by adding small
increments.
Net asset Value (NAV)
Total value of the fund's investment.
Notional principal
The amount of cash used to calculate the payments in an interest rate swap;
the principal is ``notional'' because it is never really exchanged.
Numeraire asset
Arbitrary asset chosen to measure the relative performance of an investment
in dimensionless units.
Offer price
The price a seller is asking in exchange for a security.
Open-end fund
Mutual fund where the holdings are continually reinvested and new shares
are created on demand.
Option
Security giving its holder a right, but not the obligation, to buy or
sell an asset at a set price on or before a given date.
Option class
Options having the same underlying and the same type of contract (put, call, etc).
Option series
Option from the same class having the
same exercise price and expiry date.
Out-of-the-money
Subset of an option series that has no
intrinsic value
and expires worthless.
Over-the-counter (OTC)
Non-standard exchange of goods carried out between two parties outside
the market, generally without disclosing the price to the public.
Par
Equal to the principalkeywd:principal or face value of a security.
Parameters: financial / numerical
Financial parameters entirely specify the problem; numerical parameters
only serve to control the calculation and should never affect the result.
Path dependent option
Option with a payoff depending on the price history of the underlying.
Portfolio
Set of shares and financial instruments held by a person or an organization.
Possible realizations
Outcomes of a random variable that have a finite probability to occur.
Premium
Amount that is in excess of the par value, i.e. the positive difference
between the present value and the nominal principal value.
Principal (or face) value
Amount of cash an issuer (borrower) agrees to pay at the maturity.
Principal components
Partly uncorrelated random varialbles that can explain most of the
statistical observations from the markets.
Probability
Measure of the likelihood that something will occur.
Put-call parity
Relation between the price of vanilla options with the same strike price
and expiry.
Put option
Security giving its holder the right and no obligation to sell an underlying
asset.
Random
Which cannot be predicted with certainty from the past.
Redemption date
Date when a debt security is has to be payed back, marking the end of the
lifetime of a bond.
Random walk
Unpredictable motion resulting from increments that are generally assumed
to be independent of the past (Markov property).
Reset and payment times
Beginning and end of the time interval
(accrual period)
between the payment of coupons in a bond or the exchange of interest
payments in a swap.
Risk
The possibility of something bad happening sometime in the future.
Risk premium
Reward the investors ask for taking a larger investment risk.
Security
Document proving that somebody is the owner of certain goods or has a
right to acquire them in the future.
Smile
Graph with a minimum implied volatility
for an underlying at-the-money.
Specific risk
The uncertain outcome of an investment can be divided in specific and
non-specific risks. Specific risk can entirely be eliminated through
combination of anti-correlated assets and diversification; non-specific
risk affects the entire market.
Speculator
Person who buys and sells goods in the hope of making a profit from
his view on the evolution of the market.
Split
When a growing company emits new shares to reduce the price quoted in
the market. In a 2-for-1 split, 2 new shares are exchanged for every
share that was previously owned.
Spot
The value for immediate delivery.
Stochastic
Something that includes an unpredictable random component.
Strike (or exercise) price
The price at which the underlying may be bought or sold.
Suzerain
In the Middle Ages, the suzerain was a person who owned the right over
another (called the vassal) who promised to fight and be loyal in
return for being given land to live on.
Swap (of interest rates, currency exchange rates, etc)
Contract whereby two parties agree to exchange, at known dates in the future,
a fixed for a floating set of rates without ever exchanging the principal.
Tenor of a bond
Time interval between the payment of consecutive coupons.
Term structure of interest rates
Interest rates calculated for bonds of different maturities.
Time value
Difference between the intrinsic value
and the value of an option before it expires.
Transaction costs
The cost of carrying out a trade (fees, commissions, plus the difference
between the price obtained and the middle of the bid-offer prices quoted
on the market).
Treasury rate
Interest rate payed by the central bank responsible for a given currency.
Tree
Method to approximate a dynamical system by recursively adding / subtracting
a fixed number of increments to all the possible outcomes.
Underlying
Security that parties agree to exchange under conditions in a derivative
contract.
Vanilla
Simplest form of a contract.
Venture capital
High risk investment given in return for a participation in the control
and the future earnings of a start-up company that develops a new product.
Volatility
A measure of the uncertainty of the price of an asset.
Wiener process
Markov process where the increments are normally distributed with zero
mean and a variance proportional to the time step.
Writer
The seller of an option, usually a large financial institution.
Zero-coupon bond
A bond without coupon, where the principal and the interest are paid
at the maturity date.
Zero-sum game
Game where the earning from one player exactly equals the loss from another.
SYLLABUS Previous: 10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols

 HREF="sec10.html">10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols
HREF="sec10.html">10 APPENDIX
Up: 10 APPENDIX
Next: 10.2 Notation and symbols