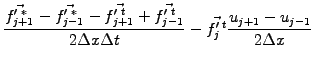
 ','..','$myPermit') ?>
SYLLABUS Previous: 6.2 Cubic-Interpolated Propagation (CIP)
Up: 6 LAGRANGIAN METHOD
Next: 6.4 Quiz
','..','$myPermit') ?>
SYLLABUS Previous: 6.2 Cubic-Interpolated Propagation (CIP)
Up: 6 LAGRANGIAN METHOD
Next: 6.4 Quiz
6.3 Non-Linear equations with CIP
Slide : [
CFL limit -
Diffusion -
Lagrangian -
Non-linear ||
VIDEO
99) echo "
modem -
ISDN -
LAN
"; else echo "login";?>
]
The same approach is applicable more generally for non-linear and vector
equations
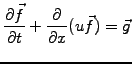 |
(1) |
where
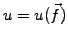 and
and
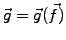 .
The problem is again decomposed in alternating phases with / without
advection describing the evolution of the function
.
The problem is again decomposed in alternating phases with / without
advection describing the evolution of the function
 |
(2) |
and by differentiation of (eq.6.3#eq.1), the evolution of the derivative
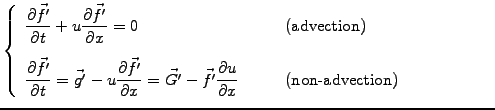 |
(3) |
Starting with the non-advection phase, the discretized function is
first evolved according to
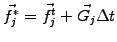 |
(4) |
where the super-script (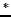 ) refers to an intermediate step. To avoid an
explicit evaluation of
) refers to an intermediate step. To avoid an
explicit evaluation of
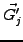 , the equation for the derivative
is computed with
, the equation for the derivative
is computed with
The advection phase can then be evolved in the same manner as before
(eq.6.2#eq.4), by shifting the cubic-Hermite polynomials along
the characteristics (exercise 6.04).
SYLLABUS Previous: 6.2 Cubic-Interpolated Propagation (CIP)
Up: 6 LAGRANGIAN METHOD
Next: 6.4 Quiz
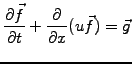


 ','..','$myPermit') ?>
SYLLABUS Previous: 6.2 Cubic-Interpolated Propagation (CIP)
Up: 6 LAGRANGIAN METHOD
Next: 6.4 Quiz
','..','$myPermit') ?>
SYLLABUS Previous: 6.2 Cubic-Interpolated Propagation (CIP)
Up: 6 LAGRANGIAN METHOD
Next: 6.4 Quiz

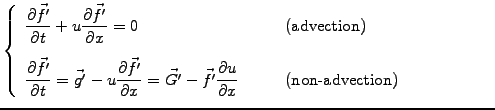
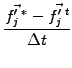
![$\displaystyle \left[
\frac{\vec{G_{j+1}}-\vec{G_{j-1}}}{2\Delta x}
-\vec{f_j^{\prime\;t}}\frac{u_{j+1}-u_{j-1}}{2\Delta x} = \right]$](s6img36.gif)